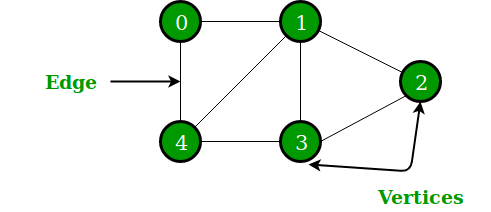
 Graph is a non-linear data structure like tree data structure. The limitation of tree is, it can only represent hierarchical data. For situations where nodes or vertices are randomly connected with each other other, we use Graph.
Graph is a non-linear data structure like tree data structure. The limitation of tree is, it can only represent hierarchical data. For situations where nodes or vertices are randomly connected with each other other, we use Graph. In today’s tutorial, we will be exploring graph algorithms. We’ll begin with an introduction to graph theory and graph algorithms. Next, we will learn how to implement a graph. Finally, we will examine common graph problems you can expect to see in a coding interview.
In today’s tutorial, we will be exploring graph algorithms. We’ll begin with an introduction to graph theory and graph algorithms. Next, we will learn how to implement a graph. Finally, we will examine common graph problems you can expect to see in a coding interview.